
Tractional retinal detachments can also occur in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy or those with proliferative retinopathy of sickle cell disease.Long term risk of retinal detachment after extracapsular and phacoemulsification cataract surgery at 2, 5, and 10 years was estimated in one study to be 0.36%, 0.77%, and 1.29%, respectively. Young age at cataract removal further increased risk in this study.

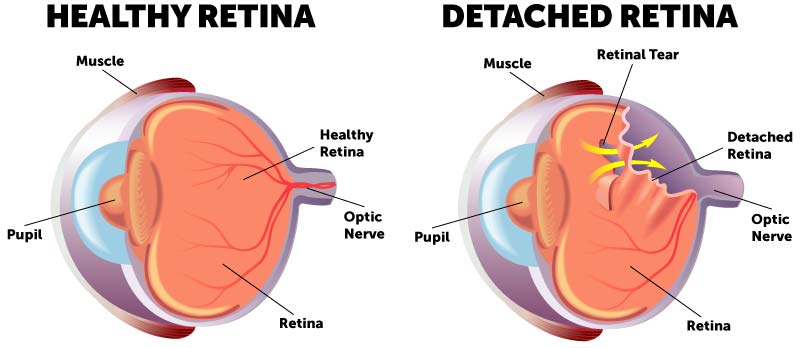
The risk may be much higher in those who are highly myopic, with a frequency of 7% reported in one study. The estimate of risk of retinal detachment after cataract surgery is 5 to cataract operations. Retinal detachment can occur more frequently after surgery for cataracts.Patients suffering from a detachment related to myopia tend to be younger than non-myopic detachment patients. Myopia is associated with 67% of retinal detachment cases. Retinal detachment is more common in those with severe or extreme myopia (above 5-6 diopters), as their eyes are longer and the retina is stretched thin.The lifetime risk in normal eyes is about 1 in 300. Detachment is more frequent in the middle-aged or elderly population with rates of around 20 in 100,000 per year. The risk of retinal detachment in otherwise normal eyes is around 5 in 100,000 per year. Tractional retinal detachment - A tractional retinal detachment occurs when fibrovascular tissue, caused by an injury, inflammation or neovascularization, pulls the sensory retina from the retinal pigment epithelium.Exudative, serous, or secondary retinal detachment - An exudative retinal detachment occurs due to inflammation, injury or vascular abnormalities that results in fluid accumulating underneath the retina without the presence of a hole, tear, or break.Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment - A rhegmatogenous retinal detachment occurs due to a hole, tear, or break in the retina that allows fluid to pass from the vitreous space into the subretinal space between the sensory retina and the retinal pigment epithelium.The tear allows vitreous fluid to seep through it under the retina, and peel it away like a bubble in wallpaper. Occasionally, posterior vitreous detachment, injury or trauma to the eye or head may cause a small tear in the retina. The retina translates that focused image into neural impulses and sends them to the brain via the optic nerve. The optical system of the eye focuses light on the retina much like light is focused on the film in a camera. The retina is a thin layer of light-sensitive tissue on the back wall of the eye. Initial detachment may be localized, but without rapid treatment the entire retina may detach, leading to vision loss and blindness. Retinal detachment is a disorder of the eye in which the retina peels away from its underlying layer of support tissue. List of terms related to Retinal detachmentĮditor-In-Chief: C. Risk calculators and risk factors for Retinal detachmentĬauses & Risk Factors for Retinal detachmentĭiagnostic studies for Retinal detachment

US National Guidelines Clearinghouse on Retinal detachmentĭirections to Hospitals Treating Retinal detachment

Ongoing Trials on Retinal detachment at Clinical Ĭlinical Trials on Retinal detachment at Google Most cited articles on Retinal detachmentĪrticles on Retinal detachment in N Eng J Med, Lancet, BMJĬochrane Collaboration on Retinal detachment Most recent articles on Retinal detachment


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
